Several scientists at the United States Geological Service (USGS) have published a report and accompanying datasets that attempts to provide a publicly accessible and comprehensive list of non-native species established in United States.
Led by Annie Simpson and Meghan C. Eyler, a team of six scientists worked six years (2013–2018). They reviewed 1,166 authoritative sources to develop a list of 11,344 unique names – most of them binomials (genus and species), a few genera, plus some viruses.
This was a Herculean effort that produced very valuable products. We are all in their dept!
Simpson and Eyler point out that knowing which species are non-native to a region is a first step to managing invasive species. Lists compiled in the past were developed to serve a variety of purposes, including watch lists for preventing invasions, inventory and monitoring lists for research and modeling, regulatory lists for species control, and non-regulatory lists for raising awareness. As a result, they are not comprehensive.
Among the sources these authors consulted in preparing the list were peer-reviewed journal articles, books, brochures, circulars, databases, environmental assessments, technical reports, graduate theses, and websites.
Data – by Region
The report also notes which non-native species were established in each of three regions: the “lower 48” states, Alaska, and Hawai`i. Not surprisingly, more than half the non-native taxa are established in the vast area (nearly 7.9 million km2) comprising the “lower 48” states – 6,675 taxa. Almost half of the total number of non-native taxa have established in the tiny geographic region (only 28,311 km2) of Hawai`i – 5,848 taxa. One-tenth as many non-native taxa – 598 – are reported as established in Alaska (1.7 million km2).
This report includes taxa that are not native to any part of the specific region, but established (naturalized) somewhere in the region. An “established” species must have at least one population that is successfully reproducing or breeding in natural systems. The list includes domesticated animals and plants introduced for crops or horticulture when the taxon has escaped cultivation or captivity and become established in the wild. Species listed range from feral hogs (Sus scrofa) to plum pox virus and citrus canker to ohia rust (Puccinia psidii).
Of the total 11,344 taxa, 157 are established in all three regions. These included 125 vascular plants (especially grasses and asters); 13 arthropods, 11 mammals; 6 birds; 3 mollusks; 1 bryozoan. One of the ubiquitous plant species is tree of heaven (Ailanthus altissima). I find it entirely appropriate that the cover photo shows this tree – the photo was taken 8 miles from my home in Fairfax County, Virginia.
Nearly three-quarters (71.4%) of the non-native species in Alaska are plant species. More than half (59.7%) of the non-native species in the “lower 48” region are also plants. Nearly all the remainder of the non-native species in both regions are some kind of animal. Fungi constitute only 1.8% of the non-native species in the “lower 48” region; all the rest of the groups (Bacteria, Chromista, Protozoa, Virus) constitute less than 1% of the non-native species recorded in either region.
By contrast, in Hawai`i, animals make up 69.7% of the listed non-native species; most are invertebrates. Plants constitute 29.8% of the Hawaiian list.
Gaps, by Taxon
The authors recognize that invertebrates and microbes are under-represented because species are still being discovered; non-charismatic and difficult-to-identify species tend to be overlooked; and the species composition of any nation in this era of globalization is constantly subject to change.
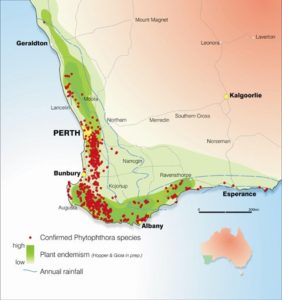
I have noted some gaps among the pathogens: the absence of some of the Phytophthora that have been detected infecting shrubs and herbaceous plants in California, e.g., Phytophthora cambivora, siskiyouensis, tentaculata; and the “rapid ohia death” pathogens, Ceratocystis huliohia and C. lukuohia. Dr. Simpson is aware of these gaps and is soliciting sources to help add these organisms – especially the various Phytophthora species – to the next version of the list.
Simpson and Eyler note that the relative geographic distribution of the list at its current state seems to reinforce three well established premises: that tropical island systems are particularly vulnerable; that higher latitudes host fewer but are not invulnerable; and that species diversity in general decreases with increasing latitude.
Comparisons to Other Databases
After standardizing the names in the list by comparing them to the Integrated Taxonomic Information System (ITIS), Simpson and Eyler also reviewed the USGS BISON database, which has more than 381 million occurrence records for native and non-native species in the U.S. and Canada, covering 427,123 different taxa. (The BISON database contains significantly more species occurrences for the U.S. than the largest invasive species database, EDDMapS, which contained 4.4 million species occurrences as of June 2018.) Simpson and Eyler had to evaluate which of these taxa met their definition of non-native, since most species occurrence records in the USGS BISON are not labeled as non-native in the original records.
Comparing the BISON and non-native lists, Simpson and Eyler found that the BISON list contained a larger number of occurrence records for non-native taxa: a total of 13,450,515.However, the BISON list does not provide complete coverage of non-native species: it includes records for 77% of list of non-native species Simpson and Eyler found in Alaska, 75% of the “lower 48” sublist, but only 37% of the Hawaiian sublist.
Simpson and Eyler state their intention to continue updating the list of non-native species, they welcome contributions to it from area experts, and they urge integration of new occurrence data into invasive species database such as EDDMapS.
Indicators of Non-Native Species Richness
Figure 3 in the report (above) maps the number of non-native taxa in BISON at the county level. Figure 4 displays the proportion of non-native to native species in BISON. Higher percentages are generally evident in coastal areas and other regional hotspots. For example, the proportion in Hawaiian counties is greater than 33%. Additional data are needed to perform a more in-depth analysis of non-native species richness and abundance.
UPDATE! New Report in the Works
In June 2021, USGS announced that it was updating its Comprehensive List of Non-Native Species Established in 3 Major Regions of the U.S. so that the document more closely aligns with the parameters of the Global Register of Introduced and Invasive Species. The new USGS dataset is to be called the US Register of Introduced and Invasive Species. The list in the current draft includes 15,364 records. About 500 of these records are in Alaska, 6,000 in Hawai`i, and 8,700 in the conterminous 48 States.
One of the lead authors, Annie Simpson, contacted invasive species experts seeking feedback and suggested additions – based on authoritative resources such as peer reviewed journal articles, pest alerts, databases, books, and technical bulletins. She sought input by 25 July, 2021.
The published version of this dataset will be made freely available on USGS’ ScienceBase (https://www.sciencebase.gov), and all reviewers will be acknowledged in the dataset’s abstract.
SOURCE
Simpson, A., and Eyler, M.C., 2018, First comprehensive list of non-native species established in three major regions of the United States: U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 2018-1156, 15 p.
The report and accompanying data tables are available here.
South African report
In an unrelated but similar development, South Africa has issued a report on its invasive species — 2017 The Status of Biological Invasions and Their Management in South Africa. The report analyzes pathways of introduction and spread; number, distribution and impact of individual species; species richness and abundance of alien species in defined areas; and the effectiveness of interventions. The report notes that 775 invasive species have been identified to date, of which 556 are listed under some national regulatory program. Terrestrial and freshwater plants number 574 species; terrestrial invertebrates number 107 species. (This total does not include the polyphagous shot hole borer, which was detected too recently.) 107 species are considered by experts to be having either major or severe impacts on biodiversity and/or human wellbeing. Alien species richness is highest in the savanna, grassland, Indian Ocean coastal belt and fynbos biomes, lower in the more arid Karoo and desert biomes. South Africans are particularly focused on the reductions in surface water resulting from plant invasions. The decades-old “Working for Water” program has two goals: providing employment and development opportunities to disadvantaged individuals in rural areas, and managing invasive alien plants.
The Status of Biological Invasions and Their Management in South Africa is available here.
Posted by Faith Campbell
We welcome comments that supplement or correct factual information, suggest new approaches, or promote thoughtful consideration. We post comments that disagree with us — but not those we judge to be not civil or inflammatory.
 Ailanthus altissima
Ailanthus altissima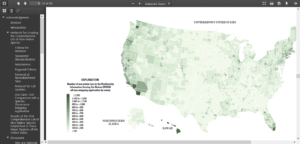













 P. ramorum-infected seedlings in a nursery; photo by USDA APHIS
P. ramorum-infected seedlings in a nursery; photo by USDA APHIS