Posted by Scott J. Cameron, former Acting Assistant Secretary for Policy Management and Budget , US Department of the Interior
In 2019 Congress passed the John D. Dingell, Jr. Conservation, Management, and Recreation Act. Among other things, it directed the Department of the Interior to “develop a strategic plan that will achieve, to the maximum extent practicable, a substantive annual net reduction of invasive species population or infested acreage on land or water managed by the Secretary.” This provision triggered a year-long process of public involvement and inter-bureau coordination. The result was a plan published in January 2021. It represents the first attempt by Interior at a Department-wide multi-taxa, multi-year approach to invasive species. It has the potential to spur integration of invasive species work across the Department’s many bureaus and to focus each bureau’s efforts on a set of common goals, strategies, and performance metrics.
While Congress’ language is open-ended, any planning exercise is constrained by the most recent President’s budget and existing law. It is up to those of us who are not, or at least no longer, executive branch employees to advocate for plans unbound by those constraints.
In that spirit, I offer eight recommendations to improve invasive species management. Four are within existing authorities; four more are outside the current budgetary and statutory framework. Many more ideas are without a doubt worth pursuing.

First, within existing funding and legal authorities, the Department has unfinished business that it can act on now.
- Secure approval of the package of categorical exclusions under the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) — now awaiting approval by the President’s Council on Environmental Quality (CEQ). Over many years agencies have documented how invasive species control improves, rather than harms, the environment. Absent an applicable NEPA categorical exclusion approved by CEQ, though, each such action needs to run the time- and money-consuming gauntlet of NEPA compliance. In the meantime, the invasive plants germinate, the invasive animals reproduce, and what might have been a localized and inexpensive problem has expanded geographically and in terms of cost and complexity. In the Fall of 2020 Interior submitted hundreds of pages of documentation on numerous practices proven to control invasive species without harming the environment. Due to time and staffing constraints at CEQ, these categorical exclusions still await action. Interior and CEQ should take prompt steps to finish them.
- Allocate to the US Geological Survey at least $10 million of the roughly $90 million remaining available to the Secretary in CARES Act appropriations for research on invasive zoonotic diseases. These are diseases like COVID-19 and West Nile virus that can move from one species to another. Many zoonotic diseases fit the definition of invasive species, since they are not native to the United States and endanger human health. In the case of COVID-19 funding is available to the Secretary of the Interior, without need for further Congressional action, from funds appropriated by the CARES Act. The availability of these funds will expire at the end of September 2021, so Interior should provide this research funding to USGS as soon as possible.
- Join the existing Memorandum of Understanding between the Western Governors Association (WGA) and the US Department of Agriculture’s Forest Service. These groups have established “a framework to allow the U.S. Forest Service (USFS) and WGA to work collaboratively to accomplish mutual goals, further common interests, and effectively respond to the increasing suite of challenges facing western landscapes.” This provides a forum to improve coordination between the States and the federal government on the management of invasive species, and Interior needs to be part of that team.
- Interior should work with USDA to accelerate and intensify efforts to systematically improve coordination between the interagency Wildland Fire Leadership Council and the interagency National Invasive Species Council. Both Councils have member agencies that practice vegetation management using similar tools and techniques, although for different purposes. The two Councils should identify a select number of initiatives in FY21 where their efforts would benefit both wildland fire management and invasive plant management .

Four steps to implement the strategic plan outside the scope of current law and the President’s Fiscal Year 2021 budget. I offer the following:
- Improve implementation of the Lacey Act program to list injurious species. There are both legislative and administrative elements to this proposal.
In a federal District Court decision on May 19, 2015, on a lawsuit filed by the Association of Reptile Keepers, the Court undid the longstanding Fish and Wildlife Service policy that the Lacey Act allowed FWS to ban interstate transport of injurious species. On April 7, 2017, the D.C. Circuit Court of Appeals upheld the District Court’s view. These rulings mean that FWS authority only applies to international commerce. Unfortunately, the court’s interpretation of the law and legislative history are reasonable, so Congress needs to amend the law to make it clear that FWS is explicitly authorized to regulate interstate commerce in injurious species. The Department of the Interior should work with the Department of Justice and the Office of Management and Budget to develop the necessary bill language and submit it to Congress.
At the same time, the FWS injurious species listing process is notoriously slow, even causing Congress to occasionally list species legislatively. The fact that these legislative initiatives have sometimes been promoted by Members of Congress who normally are opposed to more federal regulation signals just how awkward the current FWS process is. Thus there might well be strong bipartisan support to amend the Lacey Act on the interstate commerce matter. Acting on its own authority, FWS should procure an independent third party review of the injurious species listing process and ask the contractor to make suggestions for “business process reengineering” to improve and streamline current practices, along with evaluating whether higher funding or new technology is needed.
- The Bureau of Reclamation, Department of the Interior, and the Office of Management and Budget should develop legislative language to submit to Congress for the 2022 Water Resources Development Act, that explicitly authorizes an aquatic nuisance species program in the Bureau of Reclamation. It could parallel the relatively new authority enjoyed by the Army Corps of Engineers and mandate increased coordination between the two water agencies.
- Any climate change legislation pursued by Congress and the Administration should include provisions for addressing invasive species. Climate change will make some North American habitats more suitable for foreign organisms, as cold-intolerant species might be able to survive in more northern latitudes in the U.S. than previously was the case. Second, the disruptive effect of climate change on North American ecosystem structure and trophic relationships at any latitude will make those ecosystems more vulnerable to invasion. Finally, the spread of invasive species may in and of itself exacerbate climate change, such as through the increased carbon dioxide emissions from rangeland wildfires aggravated by the dominance of invasive cheatgrass.
- The Senate Committee on Environment and Public Works and the House Natural Resources Committee should each hold oversight hearings on how best to help state and local governments detect and respond to new invasive species that are not within the statutory purview of USDA/APHIS. This is a complex topic, important for both ecological and financial reasons. Over the years several attempts to address it have failed. A thoughtful review by Congress and the Administration, which perhaps would lead to passage of new statutory authority and funding, is worth exploring.
The Author:
Scott Cameron recently left the federal government, where he had served as Acting Assistant Secretary for Policy, Management and Budget at the U.S. Department of the Interior. In that capacity he oversaw Department-wide budget, invasive species, natural resource damage assessment and restoration, environmental compliance and numerous administrative functions of this $14 billion agency with 65,000 employees. Previously, Scott held other civil service job (e.g., at the White House Office of Management and Budget) & political appointments in the federal government, on the staff of the Governor of California, and on Congressional staffs. While not in government, Scott led formation of the Reduce Risk from Invasive Species Coalition.
CISP welcomes comments that supplement or correct factual information, suggest new approaches, or promote thoughtful consideration. We post comments that disagree with us — but not those we judge to be not civil or inflammatory.
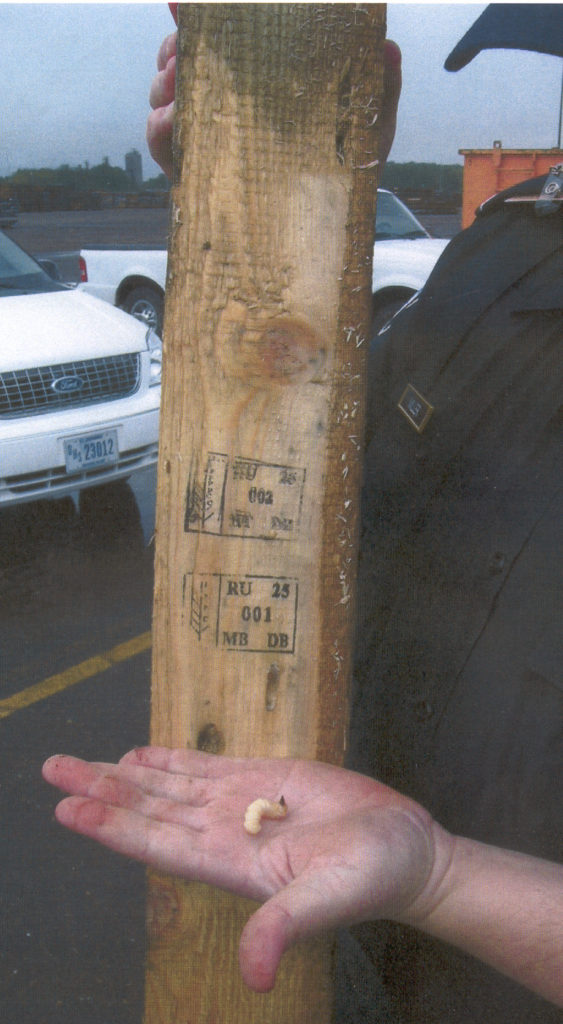
Further information on the plant pests mentioned in the photo captions can be obtained at www.dontmovefirewood.org; click the “invasive species” button.