USDA’s Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service (APHIS) has issued its annual report for Fiscal Year 2023. The report is part of an enhanced outreach effort that I believe is an effort to persuade the Congress to provide additional funds. However, as I describe below, at this summer’s annual meeting of the National Plant Board, link APHIS’ leadership stated that funding shortfalls are forcing them to curtail many programs. These include ones important to those of us concerned about threats to North American trees. I applaud this action and hope it succeeds!
The report contains some good news but I consider the overall approach depressing. Tree-killing pests continue to receive little attention. The report also emphasizes APHIS’ efforts to facilitate export of agricultural products – an understandable stance given American politics.
The opening summarizes the agency’s activities includes:
- Examples of programs targetting pests abroad, before they can reach the U.S. All are fresh fruits and vegetables;
- APHIS or staff at U.S. borders:
- Approved (cleared) 27,235 shipmentscontaining over 1.87 billion plant units (e.g., a single plant or cutting, or vial of tissue culture plantlets) and 670,811 kilograms of seeds. They intercepted 2,176 quarantine pests. (APHIS carry out these inspections at Plant Inspection Stations – separate from the port environment where DHS Customs and Border Protection (CBP) staff inspects other cargo.)
- Identified approximately 92,000 pestsfound during CBP inspections of cargo, mail, and express carrier shipments and took quick action to prevent those of concern from entering the U.S.
- Facilitated entry of regulated agricultural cargo by monitoring more than 62,000 treatments of various kinds, that is, fumigations, cold or heat treatments, and irradiation.
- Examples of APHIS’ efforts to slow pests’ spread within the country cited plant pest surveys — with coordinated responses — for approximately 45 pests. Also APHIS described funding to help citrus growers combat citrus greening.
- The report has separate subreports on the following programs: risk analysis, pest detection, “specialty crop” pests, and tree and wood pests. The last two contain information specific to our interests.
Tree and Wood Pests
This program protects forests, private working lands, and natural resources. It targets specific pests: the Asian longhorned beetle, emerald ash borer, spongy moth, and most recently the invasive shot hole borers. The report notes that numerous native, widespread hardwood tree species are vulnerable to these pests. APHIS asserts an economic justification for the program: conserving forests enhances rural communities’ economic vitality, supports forest-related industries, and maintains the ecosystem services provided by urban trees.
Unfortunately, at this summer’s annual meeting of the National Plant Board APHIS leadership said funding shortfalls forced them to pull back on all these programs.
Programs as Described in the Report
Asian Longhorned Beetle
ALB eradication aims to protect the 30% of U.S. trees that are ALB hosts. These trees support multi-billion-dollar maple syrup, timber, tree nursery, trade, and tourism industries. After reviewing the history of ALB detections, starting in Brooklyn in August 1996, the report describes APHIS’ eradication strategy as comprising surveys, regulatory inspections and quarantine restrictions, removal of infested and high-risk trees, and chemical treatment applications. In FY 2023, the program surveyed more than 763,000 trees across the four regulated areas: New York, Massachusetts, Ohio, and South Carolina. Each program is summarized.
Good news at two locations. On Long Island: only 11 new infested trees were found after a survey of 43,480 trees. In Worcester County, Massachusetts, no new infested trees were found after surveying nearly 360,000 trees. However, in Tate Township, Ohio, surveys detected 163 new infested trees. And in
South Carolina, the program is at an earlier stage — surveying a portion of the quarantine area. The program surveyed nearly 140,000 trees and removed 1,700 in FY 2023.
At the National Plant Board Meeting, Deputy Administrator Mark Davidson explained that the FY2024 appropriation cut $3.6 million from the “tree and wood pests” account. This required the agency to reduce funding for the ALB eradication program.
Emerald Ash Borer
The report summarizes the spread of EAB since its first detection in 2002 in Michigan to 37 states and the District of Columbia (APHIS does not mention EAB’s presence in five Canadian provinces.)
Saying that EAB has spread beyond what a regulatory program can control, the report notes that APHIS ended the regulatory program in FY 2021. In FY 2023 the agency continued the transition to a program relying primarily on biocontrol. In FY2023, APHIS provided parasitoids to 155 release sites – three in Canada, the rest in 122 counties in 25 states. APHIS and cooperators continue to assess their impacts on EAB populations and tree health at release sites and nearby areas. Field evaluations indicate the EAB parasitoid wasps and other EAB natural enemies (woodpeckers) are protecting regenerating sapling ash from EAB.
At the National Plant Board Meeting, Deputy Administrator Mark Davidson explained that the FY2024 appropriation cut $3.6 million from the “tree and wood pests” account. This required the agency to reduce funding for the EAB containment program – probably the biocontrol component.
Spongy Moths
Spongy moths (the species formerly called European gypsy moths) are established in all or parts of 20 eastern and midwestern states, plus the District of Columbia. APHIS and state cooperators regulate activities in the quarantine area to prevent the moths’ human-assisted spread to non-quarantine (non-infested) areas – primarily West coast states. To address the moths’ natural spread, APHIS PPQ monitors the 1,200-mile-long border of the quarantine area and adds newly infested areas to the regulated area. The USDA Forest Service – APHIS – Slow-the-Spread Foundation program has greatly reduced the moth’s rate of spread and has eradicated isolated populations.
Another component of the program aims to prevent introduction of members of the flighted spongy moth complex link from Asia. The Asian species have broader host ranges and the females can fly, so they could spread faster. A multi-nation cooperative program is designed to prevent the moths’ hitchhike on vessels coming from Asia. link APHIS supports this program through negotiations and support of CBP’s offshore vessel inspection, certification, and cleaning requirements. Canada participates in the same program.
In FY 2023, APHIS and state cooperators continued efforts to delimit possibly introductions in Washington State (no additional moths detected); and California and Oregon (initial detections in FY 2020).
At the National Plant Board Meeting, Deputy Administrator Mark Davidson explained that the FY2024 appropriation cut $3.6 million from the “tree and wood pests” account. This required the agency to reduce funding for the flighted spongy moth program.

Shot Hole Borers
The report notes that various non-native shot hole borers have been detected in several states. Their hosts include trees in forests and urban landscapes, tea plantations, and avocado orchards. The program’s focus was apparently on the polyphagous and Kuroshio shot hole borers devastating riparian habitats in southern California and urban areas in other parts of California. At California’s request, APHIS and the USDA Forest Service helped establish a working group, led by USFS, with the goal of strategically addressing both shot hole borers in California. In FY 2023, APHIS’ helped with foreign explorations for possible biocontrol agents, as well as host specificity testing.
APHIS leadership told the National Plant Board in July 2024 that it had dropped this entire program due to funding shortfalls.
Specialty Crop Pests
While much of this report concerns pests of agricultural crops (e.g., grapes, citrus, potatoes), it also summarized efforts re: Phytophthora ramorum (sudden oak death) and spotted lanternfly. APHIS says its efforts protected nursery stock production worth approximately $1.3 billion as of 2019, and tree fruit production worth approximately $1.7 billion in 2021.
Phytophthora ramorum
The report states that APHIS seeks to limit P. ramorum’s spread from affected nurseries. The agency does this via regulatory strategies. During FY 2023, 16 nurseries were governed by more stringent rules under the federal program which are imposed on nurseries that have been determined in past years to harbor P. ramorum-infected plants.
In addition, Oregon officials continued surveys of an area outside its quarantine zone because of a detection the previous year. APHIS will adjust the federal quarantine depending on the state’s findings.
The APHIS report does not discuss several pertinent events that occurred in FY2023. [For more details, read the California Oak Mortality Task Force newsletters for 2023 – posted here.
First, APHIS does not mention or discuss the implications of detection of two new strains of P. ramorum — EU1 & NA2 — in west coast forests. The presence of EU1 in a new California county (Del Norte) was confirmed in Feb 2023.
Second, the report said that Oregon is trying to determine the extent of the P. ramorum infection detected outside the state’s quarantine zone. However, it does not mention that this outbreak involves the new NA2 lineage – and that NA2 was known to be present in nurseries in the region since 2005.
The report also does not clarify that three nurseries to added to the more stringent program were so treated because SOD-infected plants were found on their premises.
Nor does the report note that at least two new naturally-infected hosts of P. ramorum were identified: Western sword fern (Polystichum munitum) and Arbutus x ‘Marina’.Koch’s postulates need to be completed on the latter so it has not yet been added to APHIS’ official host list.
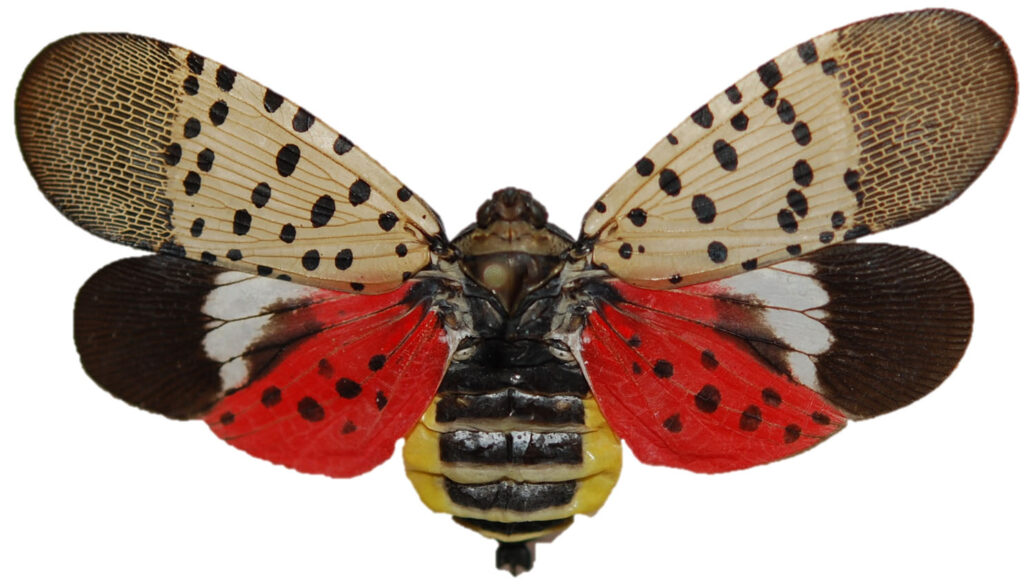
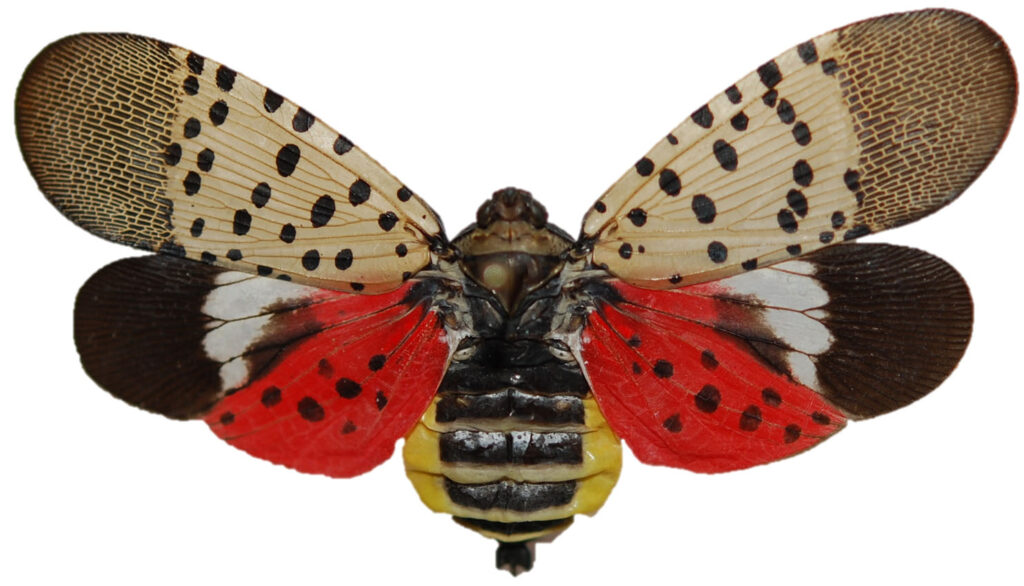
Spotted Lanternfly
Spotted Lanternfly (SLF) was found in 16 states in FY 2023. APHIS’ program enjoyed funding provided through Specialty Crop Pests and from the Plant Protection Act’s Section 7721 link ($6 million from the latter).
The report notes that APHIS still does not have enough data to determine SLF’s impacts on agriculture. Thus far, vineyards have been the most adversely affected agricultural segment, mostly due to SLF acting as a stressor to vines. Also, the sticky, sugary “honeydew” produced by SLF attracts other insects and promotes sooty mold growth. These can ruin the fruit and further damage the plant.
SLF populations are strongly linked to major transportation pathways, such as railroads and interstate highways. APHIS targets treatments and, in some areas, removes SLF’s preferred host plant (tree of heaven [Ailanthus]), from transportation hubs. The aim is to reduce the risk of SLF’ spread to new areas and to eradicate isolated infestations. In FY 2023, APHIS and cooperators treated 4,637 properties covering 6,455 acres in affected areas. However, during the National Plant Board meeting both state and APHIS officials complained to me that managers of these transportation hubs raise many barriers to their access, sharply limiting the program’s chance of success.
The program was expanded after National Environmental Policy Act-mandated environmental review. This allowed APHIS to conduct treatments in four additional states—Indiana, Massachusetts, Michigan, and Rhode Island. In addition, program cooperators identified three potential biological control organisms, one that targets the tree of heaven and two that target SLF. APHIS will continue to evaluate them and develop methods to rear them in the laboratory.
Finally, in fiscal year 2023, APHIS joined the National Association of State Departments of Agriculture and the National Plant Board to develop a national strategic plan outlining the future direction of the SLF program. With the strategic plan, PPQ aims to harmonize the approach across states to slow SLF’s spread, develop consistent outreach messaging for a nationwide audience, and more effectively use existing state and Federal resources. Continued spread of SLF despite the huge effort, rising costs of the program, and new scientific findings spurred reconsideration of the strategy.
To summarize, I hope that APHIS’ annual report will – in the future – help members of Congress and their staff understand the agency’s programs’ purpose and past successes. This increased understanding might make it easier to advocate for more funding. I am troubled, however, by the agency’s glossing over significant problems.
Posted by Faith Campbell
We welcome comments that supplement or correct factual information, suggest new approaches, or promote thoughtful consideration. We post comments that disagree with us — but not those we judge to be not civil or inflammatory.
For a detailed discussion of the policies and practices that have allowed these pests to enter and spread – and that do not promote effective restoration strategies – review the Fading Forests report at https://treeimprovement.tennessee.edu/
or